Sending Messages Using Remix¶
In this guide, we'll walk you through the process of sending cross-chain messages from the Darwinia Koi testnet to the Ethereum Sepolia testnet using the msgport protocol with Remix. No extensive smart contract development expertise is necessary — as long as you're familiar with deploying and interacting with Solidity smart contracts in Remix, you'll be able to follow along. Let's dive in!
Overview¶
This example is based on a basic Counter smart contract. The contract is simple and easy to understand. A contract with a number storage is deployed in the Sepolia testnet, and another contract named CounterSender is deployed in the Koi testnet. The goal is to call the increaseNumber() function of the Sepolia Counter from the Koi testnet CounterSender.
Prerequisites¶
Get Koi Test Token¶
Before we proceed, it's important to understand that in our cross-chain communication, the Koi network serves as the source chain while the Sepolia network acts as the destination chain. It's crucial to have this distinction in mind.
According to the msgport design, the fee for sending a cross-chain message is paid using the source chain's native token, which in this case is the Koi testnet token. Therefore, you'll need to acquire some test tokens beforehand. To do so, please use the provided faucet and ensure you add the Koi network to your Ethereum wallet, such as MetaMask.
Understand The Counter Contract¶
For ease of understanding, we'll be working with an existing contract on the Sepolia network named Counter. You can find the contract details at Sepolia Etherscan. The contract has a straightforward design; it includes a variable named number and offers a method to increment its value.
The contract at address 0xB5B87E611C742118B7e6d998458d08BB7EC54867 will serve as the destination in this tutorial. We will demonstrate how to increase the number variable by calling the increaseNumber() function through a cross-chain message from the Koi network in the upcoming steps.
Send Message From Koi¶
Prepare The CounterSender Contract¶
Create a new Solidity file named CounterSender.sol and copy the contract code provided into it. Ensure that it compiles successfully without any errors.
Deploy The CounterSender¶
After successfully compiling CounterSender.sol, the next step is to deploy it on the Koi testnet. Switch your wallet to the Koi network, if you need information on how to do this, consult the network details. The contract requires a parameter for the constructor address port, which is the address of the ORMP port, a constant across all networks. Enter 0x2cd1867Fb8016f93710B6386f7f9F1D540A60812 as the parameter and click the deploy button to deploy the contract on the Koi testnet. To monitor the transaction status, you may also visit the Koi Scan.
Send Message¶
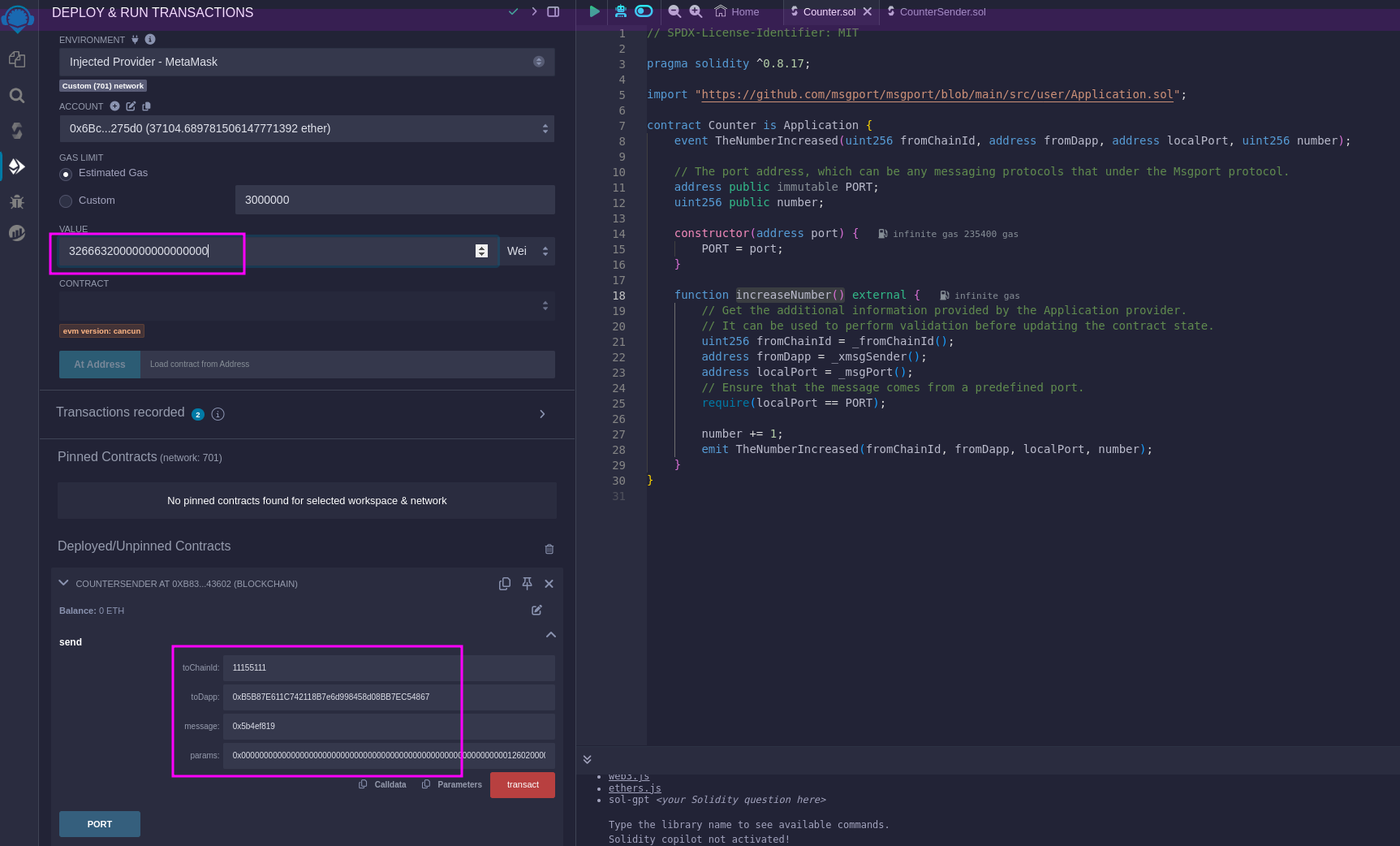
The most thrilling part of the process is invoking the send(uint256 toChainId, address toDapp, bytes calldata message, bytes calldata params) method on the CounterSender contract, which will initiate the cross-chain message transmission. The parameters for this call are somewhat complex, so let's break them down for clarity:
- value:
3266632000000000000000- The cross-chain message fee. You can easily get the value from the Msgport API for the given inputs.
- toChainId:
11155111- The Sepolia chain ID.
- toDapp:
0xB5B87E611C742118B7e6d998458d08BB7EC54867,- The address of the existing Counter contract on Sepolia.
- message:
0x5b4ef819- This is the encoded function call for
increaseNumber().
- This is the encoded function call for
- params:
0x00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000126020000000000000000000000006bc9543094d17f52cf6b419fb692797e48d275d000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000600000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000- The additional parameters for sending message. You can easily get the value from the Msgport API.
After setting up the required parameters, proceed to click the transact button to execute the send method, which will send the cross-chain message to Sepolia. Remember to note down the transaction hash 0x1fb1faa75c25ac00e5edb3fdff20b5d5bb2d4969576fc375a5855d789a2d5511 that appears in the Remix debug panel. We'll use this hash to track the status of the cross-chain operation in the following step.
Check Message Status¶
A msgport scan available to monitor the status of cross-chain messages, offering the ability to index messages by either the source chain transaction hash or the msgId. Typically, querying with the transaction hash is the most convenient approach.
Check In The Counter¶
When the message status indicator turns green and shows success, it signifies that the cross-chain message process has been completed. At this point, you can verify the Counter contract to confirm that the number value has incremented, or you can examine the contract's events for confirmation.